For most acupuncturists, the majority of our clientele is related to pain management: many people seek acupuncture because something hurts. So how does acupuncture relieve pain? In this article, I will focus on a phenomenon called the “twitch response” and a sensory receptor called the Golgi tendon organ.
Where muscles are tight, blood circulation becomes poor, and pain-inducing substances such as bradykinin and prostaglandins saturate the affected area. Chinese classics refer to this as Qi and Blood Stagnation. One of the goals of acupuncture is to improve blood circulation by relaxing muscles, tendons, ligaments, and other soft tissues. This is to “move Qi and Blood.”
When an acupuncture needle is inserted into the target area, often in the muscle near the tendon, and certain needle stimulation is rendered, you may observe a twitch response. This is when a target muscle visibly contracts briefly and then relaxes. The technique is called 雀啄 (sparrow pecking), in which a needle is maneuvered in a quick up-and-down motion within the taut strands of the target muscle.
There is another acupuncture technique specific for tendon release called 恢刺 (wide-area needling). With this technique, the target area is treated by surrounding the painful or tight area with four needles. The end result is a brief muscle contraction followed by relaxation of the muscle(s).
Trigger point therapy yields similar end results. Coincidentally, some trigger points are indeed found near where muscles and tendons meet, and some trigger points overlap known acupuncture points.
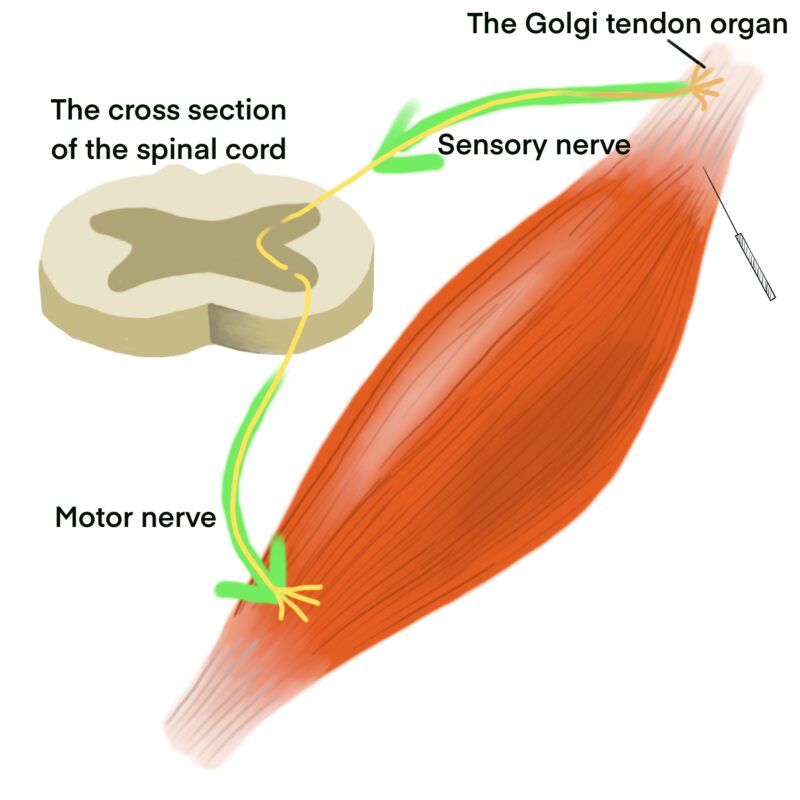
Recent literature from Japan suggests that the twitch response from acupuncture involves a proprioceptor called the Golgi tendon organ. A proprioceptor is a type of sensory receptor that sends information about the body’s movement and position to the spinal cord and the brain. As for the Golgi tendon organ, it detects tension in the tendon. The Golgi tendon then relaxes the muscle to avoid injury from excessive tension:
- Acupuncture causes a brief contraction of the muscle.
- The Golgi tendon transmits the impulse from the contraction to the spinal cord.
- Within the spinal cord, the impulse is transferred to the motor nerve.
- An inhibitory impulse is sent through the motor nerve.
- The inhibitory impulse relaxes the muscle.
After the target muscles are relaxed, blood flow to the affected area improves. The increased blood flow rids the area of pain-inducing substances. As a result, a patient feels less pain.

